
With the rapid expansion of remote work and the global distribution of digital operations, traditional perimeter-based security models are no longer sufficient. Today, businesses regularly collaborate with numerous partners both domestically and internationally, rely on cloud services, and access data centers worldwide. This interconnected environment adds complexity to securing the entire digital supply chain.
High-profile attacks like MOVEit and SolarWinds have highlighted critical vulnerabilities within supply chains. These incidents demonstrate how a single weak link can disrupt global operations and affect hundreds or even thousands of companies. As a result, ensuring supply chain security has become more important than ever.
In this article, we will explore seven key practices to help protect your organization in the face of evolving threats.
What is a Supply Chain?
In the IT industry, a supply chain encompasses all stages of building and operating systems, including design, procurement, development, sales, and ongoing software and hardware maintenance.
Common examples include:
- Corporate Supply Chains: Large companies and their subsidiaries often outsource system development to third-party vendors, leading to multiple layers of subcontractors being involved.
- Global Supply Chains: Cross-border workflows occur when development teams based overseas remotely access domestic data centers.
- Software/Hardware Supply Chains: Businesses frequently rely on third-party vendors for the software and hardware they need to run their operations.
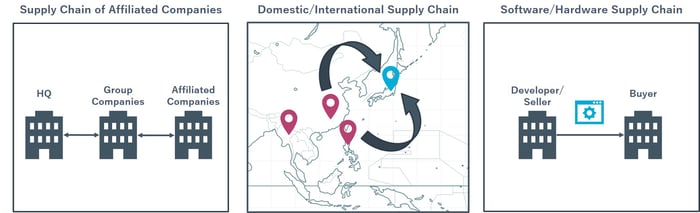
Figure1:Supply Chain Examples
The 7 Key Supply Chain Security Measures to Protect Your Business
Securing the supply chain requires a comprehensive strategy that integrates both cybersecurity and physical security measures, not just addressing third-party risks. A multi-faceted approach is essential, from vendor relationship management and regulatory compliance to protecting operational technology.
Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management (C-SCRM) plays a crucial role in identifying and mitigating risks, enhancing business continuity, and increasing supply chain visibility. While frameworks such as NIST SP 800-161r1 provide guidance, each organization must develop its own security plan.
Below are seven essential practices to help safeguard the supply chain and maintain operational integrity.
1. Implement Proper Access Management for Enhanced Security
Proper access management is critical to enhancing an organization's security and its entire supply chain. By utilizing role-based access control (RBAC), access to sensitive data and critical infrastructure is limited based on individual roles, allowing users access only to what is necessary for their duties. This reduces the potential attack surface by minimizing pathways for unauthorized users.
Additionally, adopting a zero-trust approach further strengthens security by continuously verifying users' identities and access levels inside and outside the network. Expanding access management to external partners and suppliers is essential to protect the supply chain. Prioritizing access management ensures better protection against data breaches and confirms consistent implementation of security measures across all stakeholders.
2. Secure and Effective Log Collection and Management
Proper log collection and management are fundamental to strengthening an organization's security posture. By systematically collecting and storing logs, particularly from privileged accounts with administrative rights, it becomes possible to track "who," "when," and "what" actions were taken during an incident. This capability is vital for effective incident response and accurate assessment of security breaches. Notifying users that logging is in progress can also serve as a deterrent against internal misconduct.
However, shared accounts pose significant risks. Logs from shared IDs obscure individual accountability, making it difficult to trace the source of breaches. This can delay incident response and complicate forensic investigations. Therefore, to ensure clear tracking and accountability, it is recommended to avoid using shared IDs within the organization.
3. Integrate Suppliers Into Resilience and Improvement Initiatives
Maintaining a robust security posture across the supply chain requires integrating suppliers into the organization's resilience and improvement initiatives. Promoting open communication and collaboration with key suppliers helps align security best practices, increase visibility of potential risks, and strengthen response strategies.
By including critical suppliers in incident response and disaster recovery plans, both parties can better prepare for potential disruptions or cyber threats. Jointly testing these plans improves resilience and helps identify and address any protection gaps.
Collaboration with suppliers enhances risk mitigation and the overall efficiency and security of the supply chain, contributing to more robust business continuity.
4. Design Effective Processes for Monitoring the Supply Chain
Designing effective processes for monitoring the supply chain is essential to protect the business from cyber threats and operational disruptions. A comprehensive approach should begin with thorough risk assessments of internal and external suppliers to identify vulnerabilities within the supply chain.
It is also critical to regularly monitor key components such as CI/CD pipelines, developer access, and third-party systems to ensure compliance with security standards. CI/CD pipelines, which automate code deployment through continuous integration and delivery, play a crucial role in ensuring secure and efficient software updates.
Continuous monitoring enables organizations to detect potential risks early and respond proactively, minimizing the risk of breaches.
5. Utilize Technology for Real-Time Visibility
Achieving real-time visibility is crucial for both securing and optimizing supply chain operations. By adopting technologies such as live monitoring platforms, smart tags, and connected devices, the status and location of products and assets can be continuously tracked throughout their transportation.
These innovative solutions enable the early detection of potential threats, ensure compliance with security protocols, and allow for rapid response to disruptions. In software supply chains, it is equally important to closely monitor dependencies to mitigate vulnerabilities from third-party sources.
Integrating advanced technologies into physical and digital supply chains strengthens risk management, improves operational efficiency, and enhances overall security.
6. Identify and Address Vulnerabilities Through Penetration Testing
Penetration testing is critical to identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities within the supply chain. While vulnerability scans may reveal issues like weak passwords or insecure configurations, penetration tests delve deeper, focusing on system misconfigurations and potential attack vectors.
Manual tests can uncover complex threats but may be time-consuming and risk missing critical vulnerabilities across diverse systems. Tools like binary software composition analysis, on the other hand, automatically detect vulnerabilities in third-party and open-source software components without requiring access to source code.
This distinction allows for a comprehensive security approach, addressing vulnerabilities in both systems and software, leading to a more resilient supply chain.
7. Develop a Robust Response Plan
It is crucial to develop a robust response plan to minimize the impact of cybersecurity incidents on the supply chain. A well-structured incident response plan should outline clear procedures to address threats like data breaches, malware, and third-party risks.
Assigning predefined roles, establishing escalation procedures, and implementing clear steps for isolating and eliminating threats while ensuring business recovery is essential. Regular testing and updates ensure that the plan remains effective against evolving threats.
Because supply chain security involves third-party risks, preparation, and real-time alerts enable swift response to suspicious activities. A comprehensive response plan emphasizes prevention and ensures the organization is fully prepared to effectively handle disruptions when they occur.
Safeguarding Supply Chains Against Evolving Threats
Organizations must adopt a comprehensive strategy that addresses cyber and physical threats to protect their interconnected supply chains. Implementing strict access controls, real-time visibility technologies, and thorough log monitoring can significantly reduce vulnerabilities.
Equally important is conducting regular third-party risk assessments to ensure all partners uphold high security standards. Ongoing collaboration with key vendors promotes transparency and strengthens defenses across the supply chain.
Security is not a one-time effort; it's an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance, adaptation, and improvement. Penetration testing and automated tools to identify software vulnerabilities can help uncover more serious threats.
By prioritizing resilience and regularly updating response plans, companies can stay ahead of emerging risks and ensure business continuity even as threats evolve.










