
As the threat of cyber attacks grows, there is an increasing demand for companies to have their own CSIRT or SOC systems, introduce SIEM, and implement flexible security operations that are tailored to their needs in order to detect attacks early and minimize damage.
While having such structures and systems in-house rather than outsourcing make it possible to quickly share information between responsible parties and create a monitoring system that is optimal for the organization’s environment, it requires a 24/7 monitoring team with highly specialized security personnel in order to analyze and respond to cyber attacks in real time while taking into account the latest threat information.
In this post, we will divide the challenges into two categories: “maintenance and management of SIEM infrastructure” and “security log monitoring”, then introduce “advanced ways to utilize SIEM”, citing NRI Secure’s SIEM monitoring service as one solution.
Challenges in maintaining and managing SIEM infrastructure
1. Selection of the appropriate infrastructure
First, you may be struggling to decide whether to use a cloud SIEM service or build a SIEM on-premise.
When using cloud services, depending on the region where logs are stored, care must be taken to comply with national laws and operational requirements. When building an on-premise SIEM, sizing of server resources (CPU, memory, disk, etc.) is important to ensure stable operation. SIEM requires a lot of infrastructure resources to collect and analyze large volumes of logs. Appropriate sizing requires specialized knowledge, such as calculating the processing costs of the monitoring rules to be implemented, designing the log storage period, and designing with an eye toward future increases in log volume.
In addition, it is necessary to design a log acquisition method for each product that collects logs and develop scripts to acquire logs for some specific products.
2. Improvement of the performance of SIEM
To fully utilize the functions of SIEM, it is important to improve performance with limited resources. Performance can be improved by minimizing the calculation cost of monitoring rules and optimizing SIEM parameters to suit the environment, but to achieve this, it is also important to understand the SIEM specifications in detail.
3. Version control
If you use an old version of SIEM, when you want to import or monitor new logs, the function may not be supported and you may not be able to use the latest monitoring functions. Also, if a serious vulnerability is found in the SIEM, there is a security risk that security patches cannot be applied immediately. Therefore, it is important to at least keep up with the manufacturer's supported version.
When upgrading, there is a possibility that degradation may occur and existing functions may become unusable. To prevent degradation, it is necessary to organize the functional requirements in advance, understand the release notes, and perform functional verification.
4. Detection for log collection halt
Log collection may stop for various reasons, such as changes in specifications due to version upgrades of the target equipment for log collection or changes in the log delivery route. In many cases, you will only become aware that logging has stopped when you actually need the logs, such as when an incident occurs. To prevent such situations, it is important to constantly monitor whether log collection has stopped unexpectedly.
5. Normalization of logs
Security product and device logs use the log format defined by each product, and the format and output fields are not standardized. To perform correlation analysis of logs from multiple security devices, it is essential to perform "log normalization processing" to standardize these logs into uniform fields on the SIEM. To do this, in addition to understanding SIEM itself, specialized knowledge about logs is required.
Challenges in security log monitoring and operations
1. Knowledge on alert handling
Generally, alerts from SIEM are based on mechanical detection logic, and the next action is decided and executed by the person who receives the alert. Because there are many types of security alerts, it can be difficult to interpret them without security expertise.
2. Detection rules to keep up with new threats
Cyber-attack methods are constantly evolving. To maintain a sufficient level of security measures using SIEM, it is necessary not only to create detection rules when introducing SIEM, but also to continually develop rules to detect new threats. This requires keeping up with the latest trends on a daily basis, as well as expertise in implementing detection logic in SIEM.
3. Resources to maintain a 24/7 monitoring team
Implementing detection rules is not the end of the process. In order to respond appropriately when an alert occurs, it is ideal to have a system in place where personnel with specialized security monitoring expertise monitor the system 24/7, but with a shortage of security personnel, securing such personnel is not easy.
Introduction of SIEM Monitoring Service
Without the consideration of these challenges, you may not be able to effectively utilize the SIEM even if you have put in the effort. Below, we will introduce the SIEM monitoring service provided by NRI Secure.
With our SIEM monitoring service, we install security detection rules built on our years of experience and knowledge on the SIEM infrastructure already in operation in the customer’s environment and provide real-time monitoring by security analysts 24/7. For customers who are considering introducing SIEM, we can also provide the setup and operation of a SIEM infrastructure as an option.
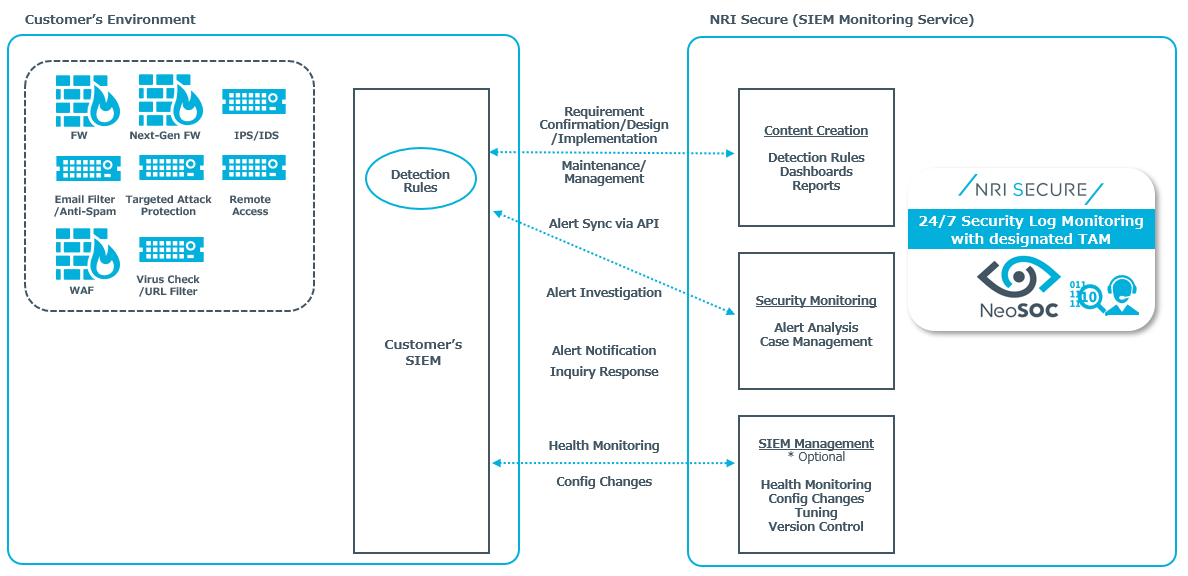
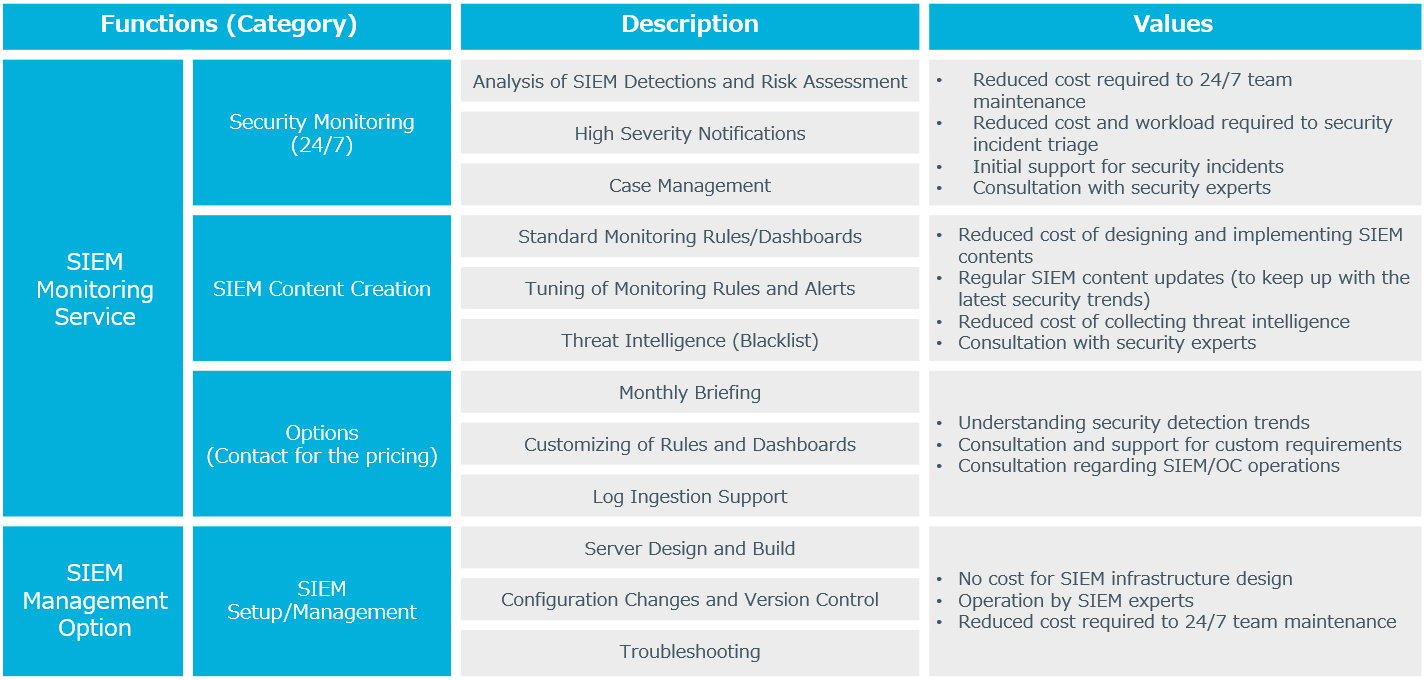
Advanced SIEM Use
There are 2 ways for outsourcing security monitoring:
1) sending logs to the security vendor and 2) storing them in your own SIEM.
1) It is difficult to consolidate logs in a SIEM for reasons such as confidential information cannot be sent, or it could be costly
2) It is relatively easy to consolidate logs because the SIEM is in-house. These logs can be used not only for general security monitoring, but also for the following purposes:
- Discover internal policy violation
- Monitor the operation status of device and applications
- Analyze access logs of website and utilize it for marketing
- Automate routine log collection
While outsourcing security monitoring, which can often be hindered by costs and resources, customers can focus on investigating their own logs or using SIEM for purposes other than security. The SIEM monitoring service makes it possible to use SIEM in various ways.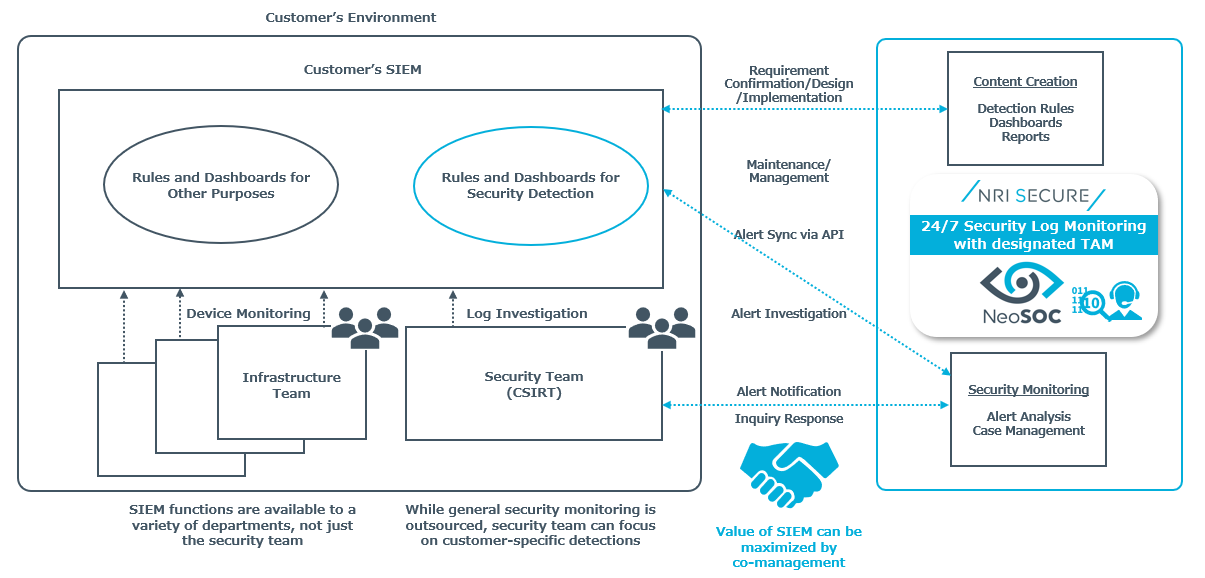
Conclusion
In this post, we introduced the challenges of security monitoring using SIEM, SIEM monitoring service, and examples of advanced SIEM use.
There is no doubt that SIEM is an effective security tool against cyber-attacks, which are constantly evolving. However, we hear often that there are many challenges using SIEM and many customers with SIEM implemented need support to manage the operation.
A realistic solution to maximizing the value of SIEM is to outsource tasks such as security monitoring that are difficult to handle in-house, while at the same time taking on areas that are difficult to outsource, such as log investigations containing confidential information.
In addition, we provide consultation on defining requirements such as which devices should be monitored and specific detection rules. If you have any questions or concerns, please feel free to contact us.










