
There is no end to information leakage incidents due to internal fraud. It is strongly recommended to review the status of countermeasures for preventing information leakage by insiders of the organization. Internal fraud countermeasures range from technically preventing crimes to physical management and employee compliance.
We have explained internal fraud countermeasures in “Learn How to Fight Against Internal Fraud from Information Leak Cases” in the past. This article is posted to explain internal fraud countermeasures from a different perspective and support it.
Learn How to Fight Against Internal Fraud from Information Leak Cases
Introduction
Information leakage due to internal fraud tends to increase the number of leaked personal information compared to cyber attacks from the outside. However, it seems the countermeasures against internal fraud are often overlooked or postponed with belief that mankind is fundamentally good.
In this article, we will organize the viewpoint of internal fraud countermeasures and explain them based on specific examples. They should help you to review measures against internal fraud in your organization.
Internal Fraud
Looking at “10 Major Security Threats” announced annually by Information-technology Promotion Agency, Japan (IPA), “Information Leakage by Internal Fraudulent Acts” ranked 5th in 2019, 2nd in 2020, and 6th in 2021 as threats to the organization, which shows that the threat seems to remain highly ranked.
In response to threat of internal fraud, IPA has established five basic principles for internal fraud prevention in the “Guideline for the Prevention of Internal Improprieties in Organizations”.

Figure1:Basic policies to prevent internal improprieties
Excerpt from IPA “Guideline for the Prevention of Internal Improprieties in Organizations”
To realize these, it is a prerequisite for management and the general manager to formulate a “basic policy of the organization”. On top of that, the person in charge of the site and related departments, such as the information system department, are required to take necessary measures.
Based on the “Internal Impropriety Check Sheet” in Appendix II of the guideline, the relationship between countermeasures and the department in charge is summarized below:
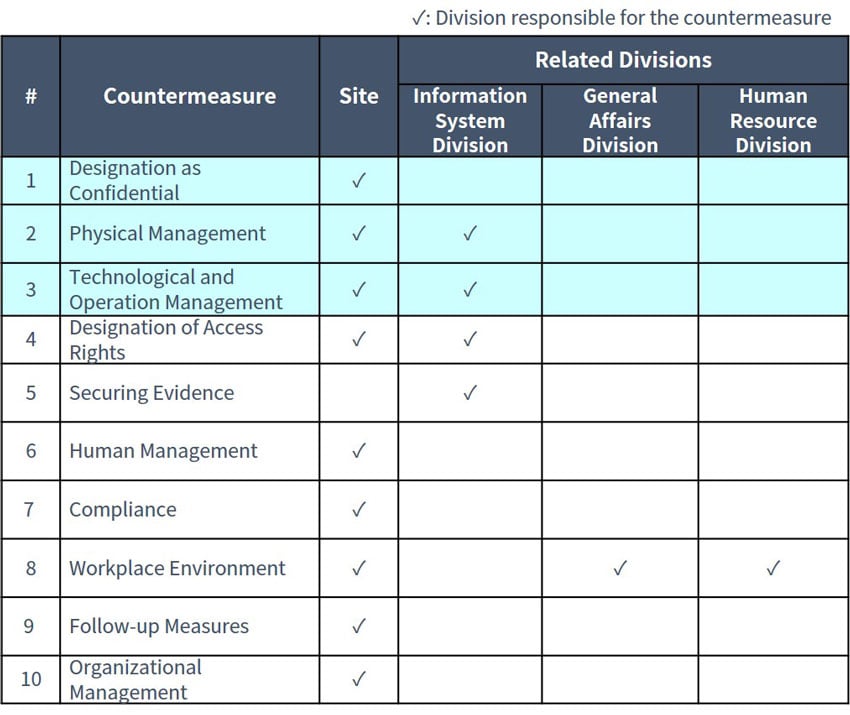
Figure2: Relationship between countermeasures and related divisions (Summarized by NRI Secure based on “Internal Impropriety Check Sheet”)
In the past, we summarized countermeasures for internal fraud realized by our privileged ID management solution in “Learn How to Fight against Internal Fraud from Information Leak Cases”.
It corresponds to “Designation of Access Rights” and “Securing Evidence” in the above table. Appropriate "Designation of Access Rights” makes it difficult to commit crimes by preventing unexpected operation of information systems. Furthermore, with thorough “Securing Evidence”, it is possible to prevent an excuse by the insider.
In this article, we introduce examples of measures recommended for sites and information system departments regarding “Designation as Confidential”, “Physical Management” and “Technological and Operational Management” from the viewpoint of not creating an environment where internal fraud is possible.
Security Measures against Internal Fraud
Classification of Data
Classifying the Importance of Information
When considering measures against internal fraud, it is essential to set the importance of information and take measures accordingly. The following is an example how the importance can be defined:
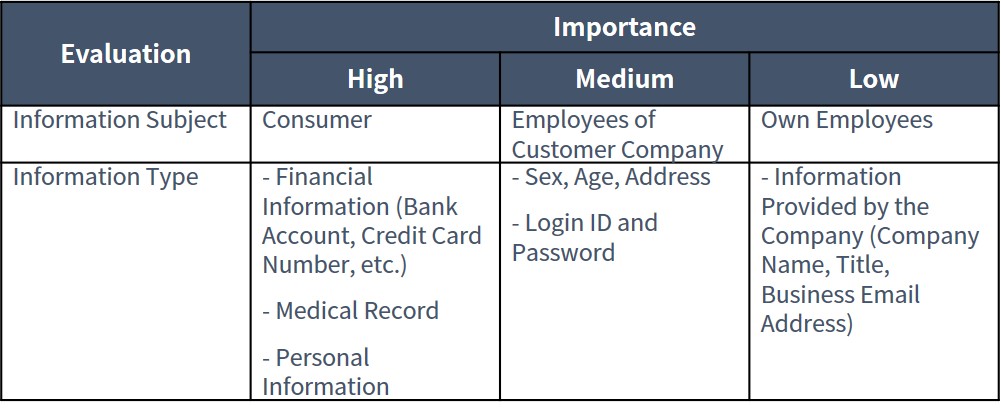
Figure3:Examples of classification of the importance of personal information
Definition of Classification
After setting importance based on the above criteria, classification of information needs to be determined.
For example, the personal information of “Consumers”, which is highly important, is defined as information limited to a specific person in the organization (“Restricted”). Personal information of “Own Employees” is defined as information that is limited to employees only (“Internal Use Only”). Data including such information will be stored in a folder that can be accessed only by authorized personnel.
In addition, it is desirable for the creator of important information to select the above classification according to the policy of the organization and to confirm the validity of the selection with the supervisor.
Indication of Definition
It is recommended to display classification on the document to prevent anyone who obtains a “Restricted” document from storing it in a location accessible to a non-related party by accident.
Physical Measures
Restrictions on confidential information transfer
The place where important information is handled should be physically isolated so that only those who have been authorized can enter the room. Generally, a special room called the production terminal room is prepared.
To limit the number of people accessing the production terminal room and to be able to track them later, it is effective to allow them to enter the room by using an ID card or biometric authentication issued to the individual.
Additionally, it is recommended not to issue the account necessary for taking out important information to the person in charge. Require two or more people within the room to prevent internal fraud by the person in charge to authorize the entry.
Property Management of Computer and USB Device, etc.
It is desirable to physically prevent information, such as a computer, from being taken out with wire locks.
It is also effective to install a surveillance camera so that people entering and leaving the production terminal room can be checked to prevent information from being taken out.
Storage mediums, such as USB drives, necessary for business should be stored in a locked cabinet. Manage the lending of each device and recommend that the lending manager should assign a person in charge of the important information handling independently.
Access Restriction of Personal Smart Phone and USB Device, etc.
It may be difficult to check personal belongings or supervise the work of handling important information every time someone enters the production terminal room. It is important to prevent information from being taken out via personal devices, such as a smartphone, USB drive, SD cards, etc.
In that case, a useful measure is to physically block the USB port of the computer that handles important information, or alternatively block the access systematically via BIOS settings or dedicated software. It is desirable to limit the authority that can disable settings on the system to those who have separated duties.
On the other hand, it is recommended that the use of storage media is limited to those approved by the organization in case the use of a storage media, such as USB drives, are required for business purposes.
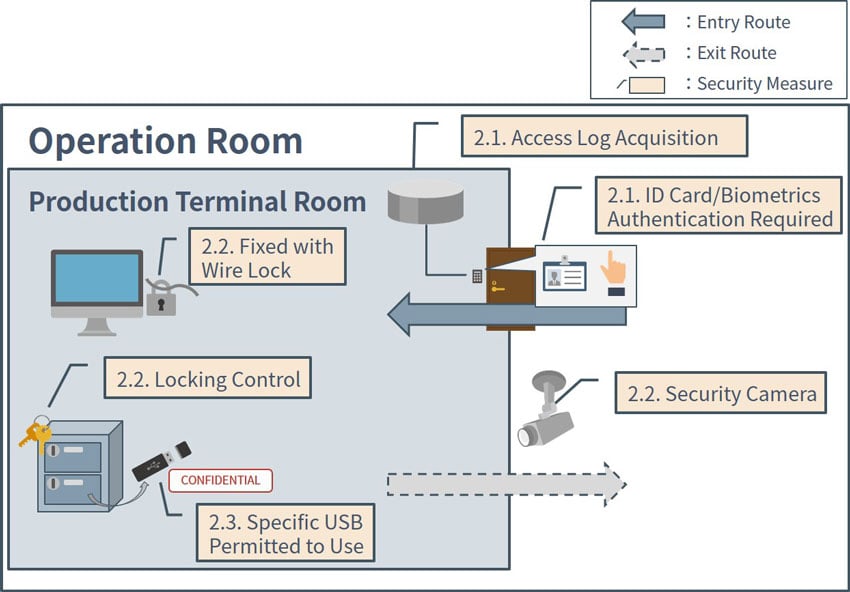
Figure4: Restrictions on taking out important information in the production terminal room
Data Erasing at Disposal of Information Asset and Memory Medium
Formatting as a computer function is not sufficient for deleting information. It is desirable to physically destroy data storage, such as HDD, or delete the data using dedicated software, if it is difficult.
It is also recommended not only to submit a disposal certificate, but also to select a business operator who can provide a photo to confirm that is has been physically destroyed when outsourcing disposal to a third-party vendor. In the past, there have been cases in which employees of disposal companies illegally took data storage to be disposed of, leading to large-scale information leakage. This could have been prevented if the security measures above were implemented.
Technology/Operation Management
Restriction on Use of Online Services
In general, internet access from a computer in the production terminal room should not be allowed.
In case this is difficult, it is recommended to restrict internet access to allow only specific websites by web filtering and limit the use of cloud services that are not permitted by CASB. Regularly check access to websites and cloud usage that are not business related. In particular, file sharing software, social media, external online storage services, etc. may be used for unauthorized data transfer, so extra caution is required.
Life Cycle Management of Information
When important information is taken from the production terminal room, it is necessary to confirm validity of the information and ensure that it is properly disposed of in the end when it is no longer needed.
For example, the validity of information to be taken out using USB drives can be checked by verifying the application form of transfer (date, time, applicant name, file name, etc.) and the record of asset management software (date, time account ID, file name, etc.). The security level can be improved by limiting verification to those who have separated duties.
In addition, USB device used should be returned to the administrator immediately after work, and the administrator should confirm that the data has been deleted.
Conclusion
In recent years, cyber attacks have become more sophisticated and we tend to focus on countermeasures, but we should also implement internal fraud countermeasures that can lead to information leaks. Implementing internal fraud countermeasures also help reduce the impact of cyber attacks.
In this article, we explained “Classification of Data”, “Physical Measures”, and “Technology/Operation Management”. In “Classification of Data”, we explained the importance of classifying the information and displaying it in the electronic documents. In “Physical Measures”, we have illustrated measures to prevent unauthorized move of information devices that contains important information. Finally, in “Technology/Operation Management”, we introduced examples of limiting the leakage route of important information via the internet and managing the transfer.
We hope that you find this article useful for internal fraud prevention in your organization.










